A literal that represents a changeable quantity is called a variable.
According to English Language, the meaning of the word “variable” is changeable. The mathematics is all about the numbers. So, the variables are used to represent the changeable quantities and they are denoted by literals.
The variables are used in two cases.
Let’s learn both cases to understand how the variables are used in algebraic mathematics.
A variable is used to denote the changeable quantity.
Take, the letter $t$ is used to represent the total number of apples falls on the ground. Initially, there is no apple on the floor. Hence, it is denoted by $t = 0$ algebraically.
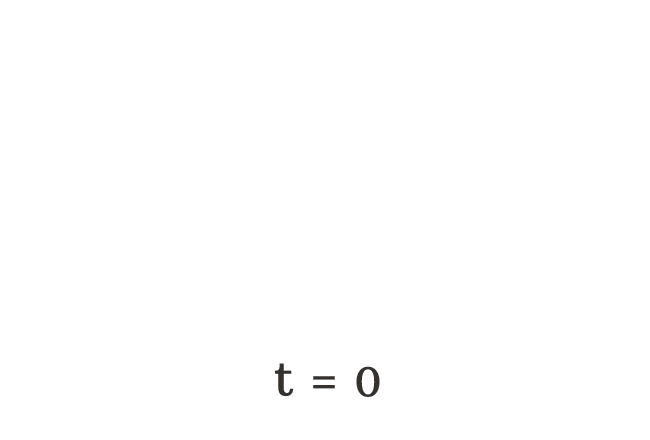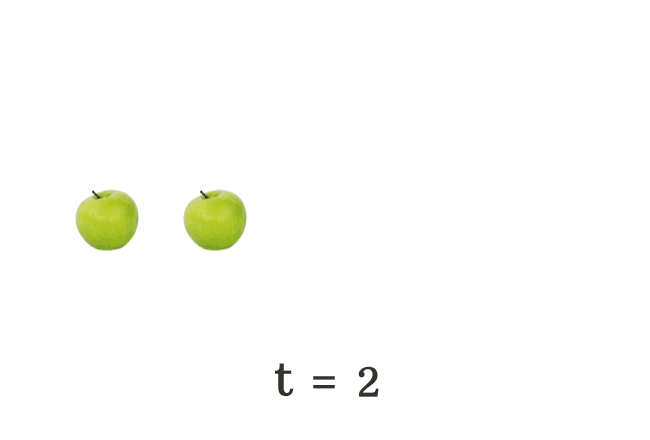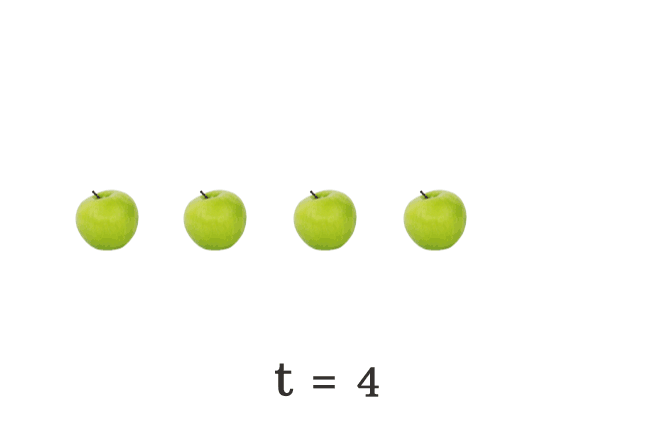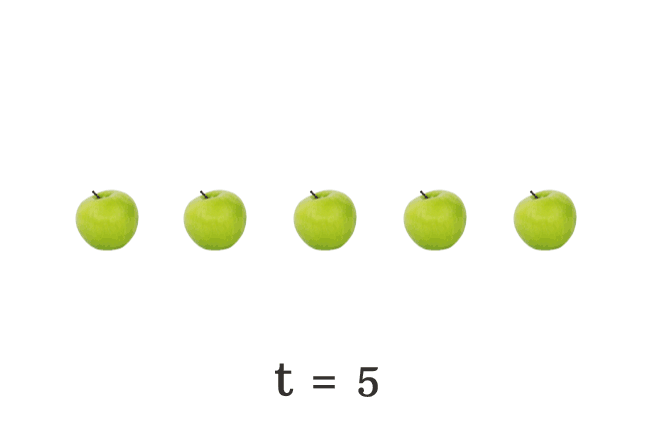
$(1) \,\,\,\,\,\,$ $t \,=\, 0$
$(2) \,\,\,\,\,\,$ $t \,=\, 1$
$(3) \,\,\,\,\,\,$ $t \,=\, 2$
$(4) \,\,\,\,\,\,$ $t \,=\, 3$
$(5) \,\,\,\,\,\,$ $t \,=\, 4$
$(6) \,\,\,\,\,\,$ $t \,=\, 5$
The total number of apples falls on the floor is changing every time. Hence, the literal $t$ is called a variable.
A variable is also used to represent an unknown quantity.
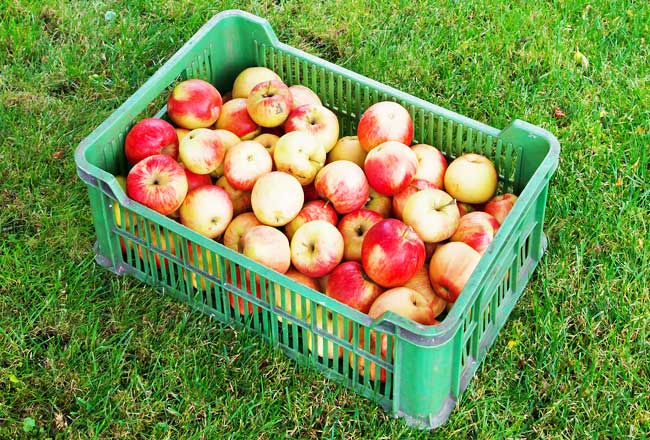

There are some apples in a box but we don’t know exactly how many apples they are. Hence, the quantity is denoted by a literal. For example, $m$.
Can you guess how many apples they are?
You guess a number and I guess a number. It is changed for every person. So, an unknown quantity is considered as a changeable quantity. Therefore, a literal number that represents an unknown quantity is usually called as a variable. In this case, $m$ is a variable.
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2025 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved