X-Axis of Two Dimensional Cartesian coordinate system
Formula
A horizontal number line that used as a reference to determine the position of each point in a plane is called the x-axis of two-dimensional cartesian coordinate system.
What is the x-axis?
There are so many points on a plane. So, a horizontal number-line is required as reference to determine the exact position of every point from origin in horizontal direction, and the number line is called the horizontal axis of two dimensional cartesian coordinate system.
Let’s learn what the $x$-axis really is on 2D space and also know how to use the $x$-axis in mathematics from the following geometric explanation by the $x$-axis on a graph.
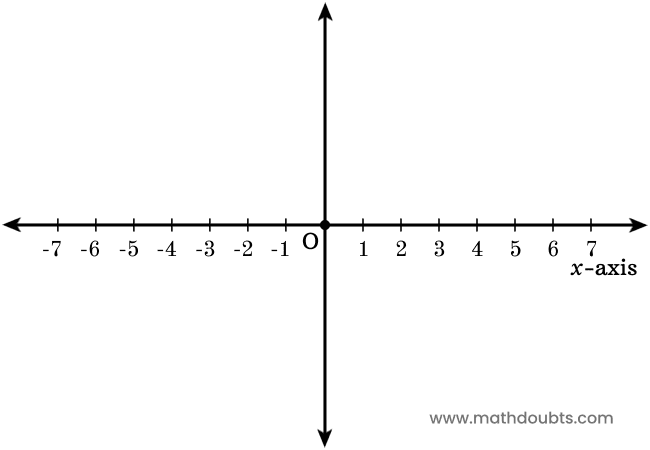
In geometry, the position of each point in horizontal axis’s direction is generally denoted by a letter $x$. So, the horizontal axis is also called as $x$-axis of two dimensional cartesian coordinate system.
Divisions
The vertical line divides the horizontal axis into two equal parts in a plane. So, the $x$-axis has two parts and its middle point is the origin of bi-dimensional cartesian coordinate system. Now, let’s know each side of the horizontal $x$-axis in detail with understandable visual examples.
Positive x-axis
Every language (except few) is usually written from left to right and it is a natural reason for considering each division from origin to right side of $x$-axis as positive. So, the positive numbers are used to denote each division on number line from origin to right side and that number line is called the positive $x$-axis.
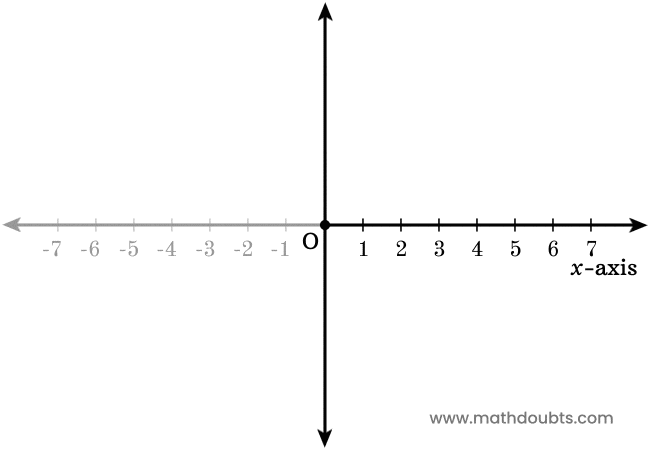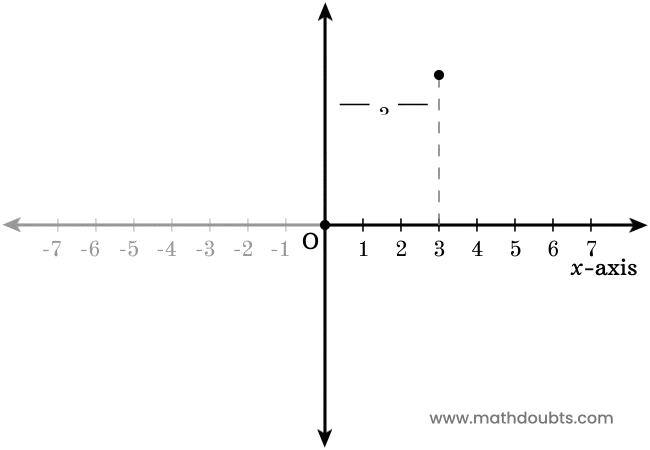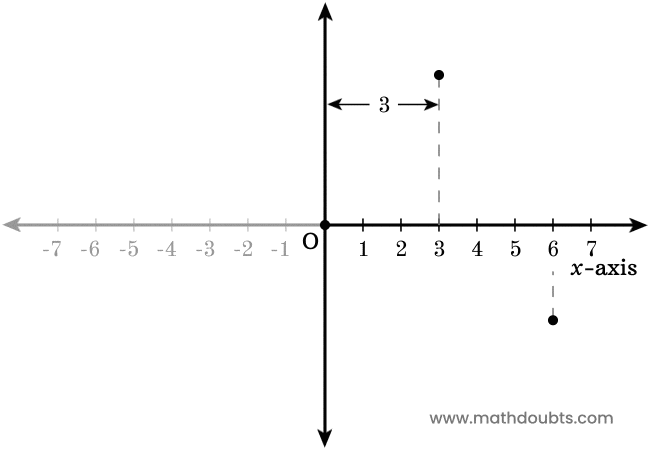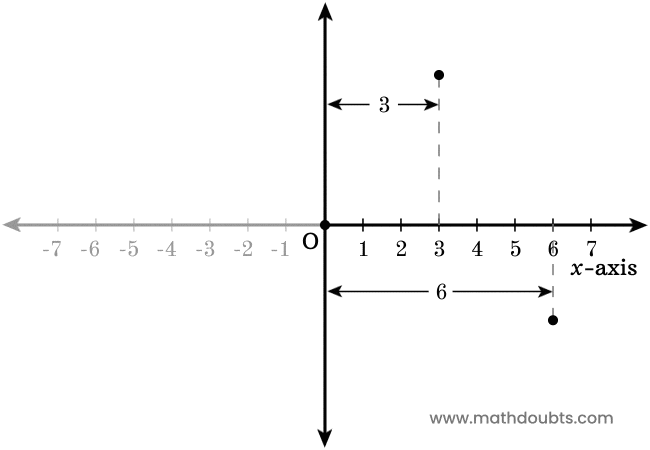
Now, let’s learn how to use the positive $x$-axis to find the position of each point horizontally.
- There is a point above the positive $x$-axis in the plane. Now, draw a perpendicular line to $x$-axis from the point. It is apparent that the point is $3$ units away from the origin.
- There is another point in the plane and it is below to the positive $x$-axis. Now, draw a perpendicular line to $x$-axis from the point. It is evident that the point is $6$ units away from the origin.
In this way, you can find the exact position of each point in the horizontal $x$-axis direction in a plane.
Negative x-axis
The numbers from origin to left side is considered as negative. So, the negative numbers are written on divisions of number line from origin to left side and that number line is called the negative $x$-axis.
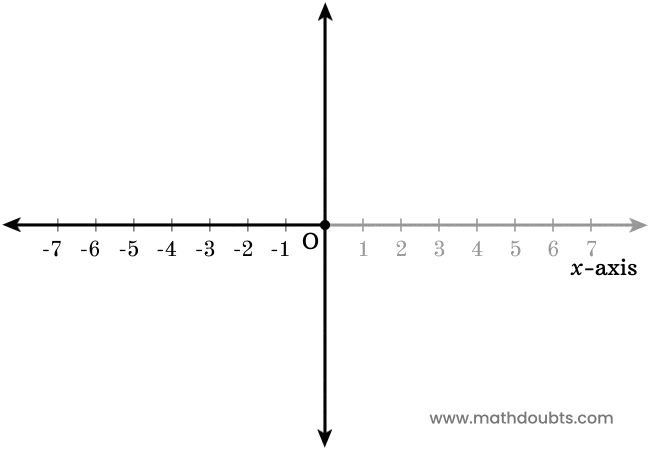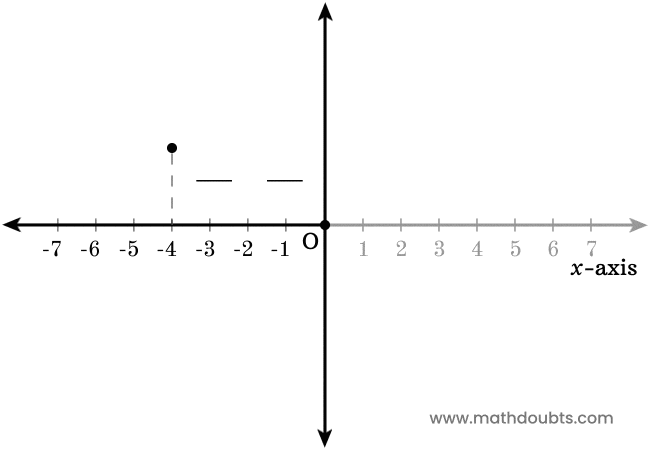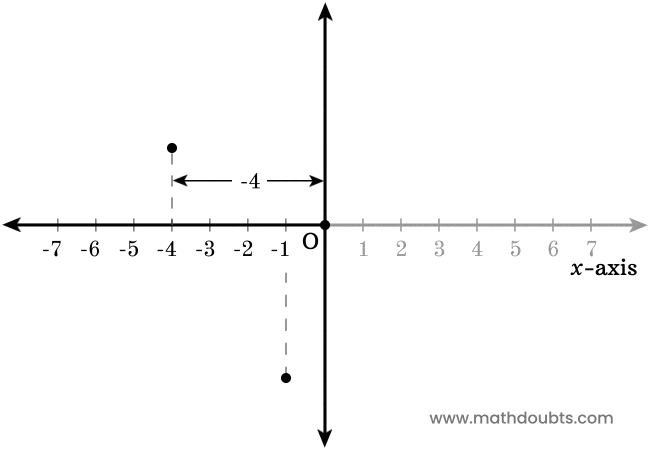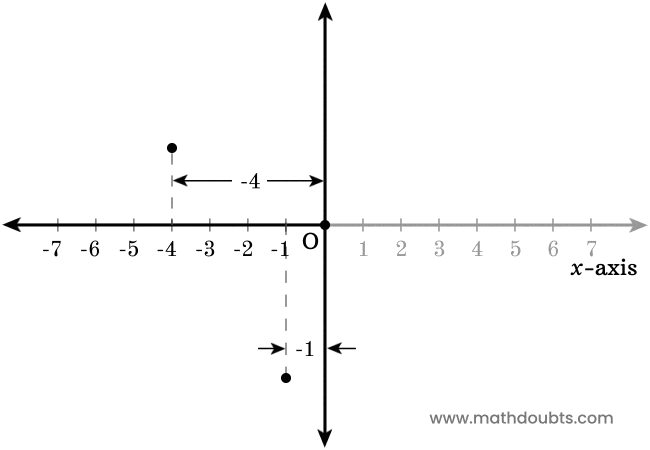
Now, let’s learn how to use the negative $x$-axis to find the position of each point in horizontal direction.
- There is a point above the negative $x$-axis in the plane. Now, draw a perpendicular line to $x$-axis from the point. It is evident that the point is $-4$ units away from the origin.
- There is another point in the plane and it is below to the negative $x$-axis. Now, draw a perpendicular line to $x$-axis from the point. It is apparent that the point is $-1$ units away from the origin.
In this way, you can find the exact position of every point in the horizontal $x$-axis direction in a plane.
The above explanation with graphics helped you how to use $x$-axis on a graph in two dimensional cartesian coordinate system. Now, start practice on a graph to find the position of every point with the help of $x$-axis on a two dimensional space.
