The value of trigonometric tangent of an angle, made by a straight-line with horizontal axis in anticlockwise direction, is defined slope of the straight line.
Straight lines are often appeared in a plane by making some angle with horizontal axis. The angle of the straight line has a direct relation with the slope of the straight line. This property shows a way to evaluate slope of a straight line from its angle, made with horizontal axis in anticlockwise direction.
Assume, AB↔ is a straight line in a plane and also assume it makes some angle with horizontal axis in anticlockwise direction.
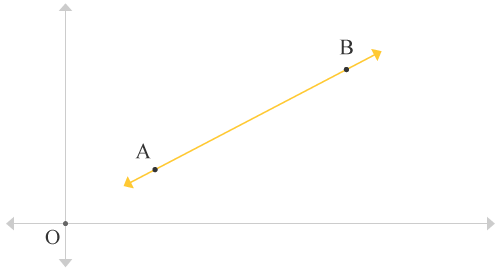
Draw a horizontal line from point A towards right side and also draw a vertical line from B downwards. The line drawn from point A and the line drawn from point B meet at a particular point on the plane.
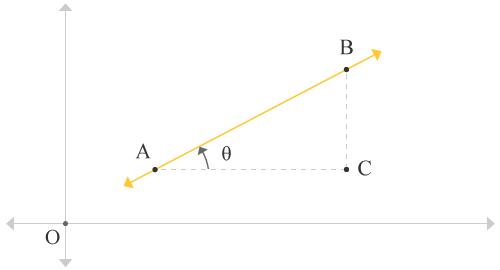
The intersecting point of two perpendicular lines is assumed to call point C. Thus, the line AB↔ forms a right angled triangle ΔBAC. Assume, the angle of a triangle ∠BAC is θ. It means, the straight line AB↔ made an angle θ in anticlockwise direction with a horizontal line AC‾ (parallel to horizontal axis).
According to principle definition, the value of tangent of angle is known slope of the straight line. It means, slope of the straight line is written as tanθ mathematically. In mathematics, the letter m is used to denote the slope of the straight line.
Therefore, the slope of the straight line is (m) = tanθ
This mathematical relation is mainly used to evaluate slope of the straight line from the angle, made by the same line.
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2025 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved