$\sec^2{\theta}-\tan^2{\theta} \,=\, 1$
The subtraction of square of tan function from square of secant function equals to one is called the Pythagorean identity of secant and tangent functions.
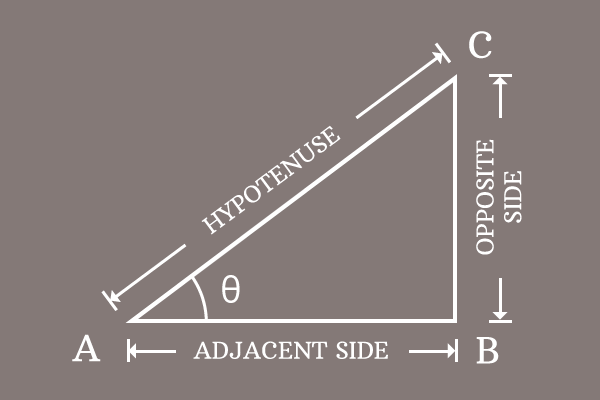
In trigonometry, the secant and tangent are two functions, and they have a direct relation between them in square form but their relationship is derived from Pythagorean theorem. Therefore, the relation between secant and tangent functions in square form is called the Pythagorean identity of secant and tangent functions.
The subtraction of the tan squared of angle from secant squared of angle is equal to one and it is called as the Pythagorean identity of secant and tangent functions.
$\sec^2{\theta}-\tan^2{\theta} \,=\, 1$
The Pythagorean identity of secant and tan functions can also be written popularly in two other forms.
Remember, the angle of a right triangle can be represented by any symbol but the relationship between secant and tan functions must be written in that symbol.
Learn how to prove the Pythagorean identity of secant and tan functions in mathematical form by geometrical method.
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2025 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved