Properties of Right triangle when angle equals to 30°
Properties
There are three basic notable properties in a right triangle when its angle equals to $30$ degrees.
- The length of opposite side is equal to half of the length of hypotenuse.
- The length of adjacent side is equal to $\small \sqrt{3}/{2}$ times of the length of hypotenuse.
- The third angle of right triangle is $\small 60^°$.
Theorem
$\Delta POQ$ is a right triangle and its angle is $30^°$. Assume, the length of hypotenuse is equal to $d$.
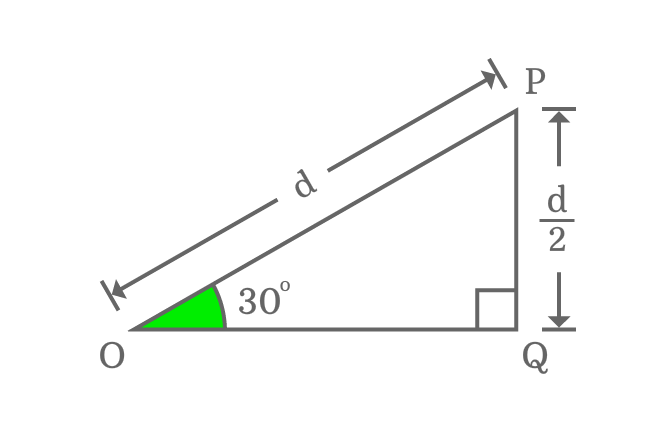
Then, the length of opposite side is exactly equal to half of the length of the hypotenuse.
$Length \, of \, Opposite \, side$ $\,=\,$ $\dfrac{Length \, of \, Hypotenuse}{2}$
$\implies$ $Length \, of \, Opposite \, side$ $\,=\,$ $\dfrac{d}{2}$
The lengths of opposite side and hypotenuse are known. They can be used to calculate the length of adjacent side (base) mathematically by Pythagorean Theorem.
${OP}^2 \,=\, {PQ}^2 + {OQ}^2$
$\implies d^2 \,=\, {\Bigg(\dfrac{d}{2}\Bigg)}^2 + OQ^2$
$\implies d^2 \,-\, {\Bigg(\dfrac{d}{2}\Bigg)}^2 \,=\, OQ^2$
$\implies OQ^2 \,=\, d^2 \,-\, {\Bigg(\dfrac{d}{2}\Bigg)}^2$
$\implies OQ^2 \,=\, d^2 \,-\, \dfrac{d^2}{4}$
$\implies OQ^2 \,=\, d^2 \Bigg[1 \,-\, \dfrac{1}{4}\Bigg]$
$\implies OQ^2 \,=\, d^2 \Bigg[\dfrac{3}{4}\Bigg]$
$\implies OQ^2 \,=\, \Bigg[\dfrac{3}{4}\Bigg]d^2$
$\implies OQ \,=\, \sqrt{\Bigg[\dfrac{3}{4}\Bigg]d^2}$
$\implies OQ \,=\, \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}d$
$\implies OQ \,=\, \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \times d$
$\implies OQ \,=\, \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \times OP$
$\therefore \,\, Length \, of \, Adjacent \, side \,=\, \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \times Length \, of \, Hypotenuse$
Proof
The properties of right angled triangle can also be proved geometrically by constructing an example triangle with an angle of $30$ degrees.

- Firstly, draw a straight line horizontally from point $\small R$.
- Use protractor and draw a straight line from point $\small R$ but it should make an angle of $\small 30$ degrees with horizontal line.
- Take compass and a ruler, then set compass to $\small 10 \, \normalsize cm$. After that, draw an arc on $\small 30$ degrees line from point $\small R$. They both get intersected at point $\small S$.
- Draw a perpendicular line to horizontal line from point $\small S$ and it intersects the line at point $\small T$. Thus, a right triangle ($\small \Delta SRT$) is constructed geometrically.
Let us study the geometrical relations between sides of a right triangle when its angle is $30^°$.
Property
The length of opposite side (perpendicular) equals to half of the length of hypotenuse when angle equals to $30$ degrees.

Now, take a ruler and measure the length of the opposite side ($\small \overline{ST}$). You observe that the length of opposite side $\small \overline{ST}$ is $5 \, cm$ exactly.
Actually, it is half of the length of the hypotenuse. It is possible only when the angle of a right triangle equals to $30^°$.
So, remember that the length of opposite side is always equal to half of the length of the hypotenuse when the angle of right angled triangle is $30^°$.
Property
The length of adjacent side (base) equals to $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ times of the length of hypotenuse when angle equals to $30$ degrees.
Measure the length of the adjacent side $\small \overline{RT}$ by ruler and you observe that the length of the adjacent side is equal to $8.65 \, cm$. Later, calculate the length of the adjacent side in theoretical method to compare difference between them.

$Length \, of \, Adjacent \, side$ $\,=\,$ $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \times Length \, of \, Hypotenuse$
$\implies$ $Length \, of \, Adjacent \, side \,=\, \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \times 10$
$\implies$ $Length \, of \, Adjacent \, side \,=\, 8.66025\ldots$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\,$ $Length \, of \, Adjacent \, side \,\approx\, 8.66 \, cm$
Theoretically, the length of adjacent side is $8.66 \, cm$ approximately and geometrically, it is $8.65 \, cm$. They both are equal approximately in mathematics.
It proves that the length of adjacent side is equal to $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ times of length of hypotenuse when angle of right triangle is equal to $30^{°}$.
