$y-y_{1} \,=\, \dfrac{y_{2}-y_{1}}{x_{2}-x_{1}}(x-x_{1})$
It is an equation of a straight line when a straight line intersects both axes with $x$ and $y$ intercepts.
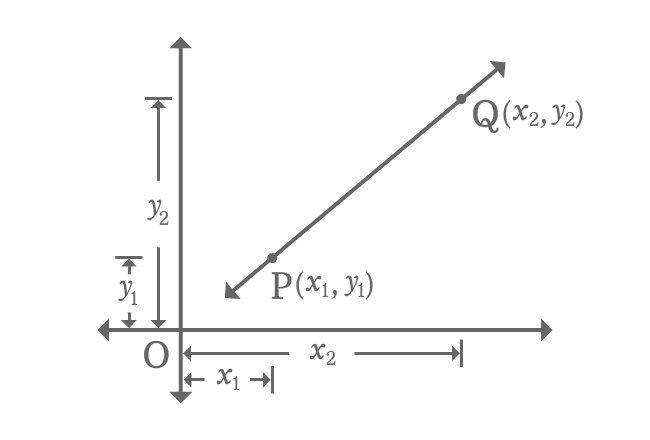
There is a straight line with some inclination in Cartesian coordinate system. $P$ and $Q$ are two points on the straight line.
The coordinates of the point $P$ are $x_{1}$ and $y_{1}$, and it is represented as $P(x_{1}, y_{1})$. Similarly, the coordinates of the point $Q$ are $x_{2}$ and $y_{2}$. It is geometrically written as $Q(x_{2}, y_{2})$ in mathematical form.
Now, it is time to derive the equation of straight line in two point form. The concepts slope of straight line and tan of angle are used here to derive the linear equation in algebraic form.
Draw a perpendicular line to $x$-axis from point $Q$ and also draw a parallel line to $x$-axis from point $P$. The two lines are intersected at point $R$.
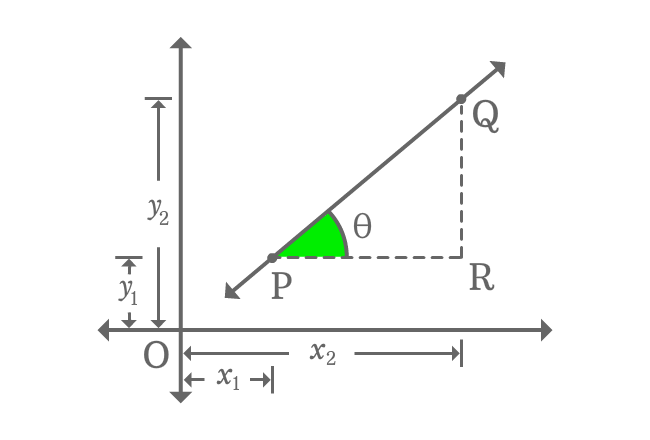
A right triangle, known as $\Delta RPQ$ is formed geometrically. Take the angle of this triangle is theta and it is also inclination of straight line.
Evaluate slope of straight line $\overleftrightarrow{PQ}$.
$m \,=\, \tan{\theta}$
According to $\Delta RPQ$
$\tan{\theta} \,=\, \dfrac{QR}{PR}$
$\implies \tan{\theta} \,=\, \dfrac{OQ-OR}{OR-OP}$
$\implies \tan{\theta} \,=\, \dfrac{y_{2}-y_{1}}{x_{2}-x_{1}}$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\, m \,=\, \dfrac{y_{2}-y_{1}}{x_{2}-x_{1}}$
$S$ is any point on the straight line $\overleftrightarrow{PQ}$ and its coordinates are $x$ and $y$. Draw a perpendicular line to side $\overline{PR}$ from $S$. It formed another right triangle, known as $\Delta TPS$. The angle of $\Delta TPS$ is also theta due to similarity of the triangles $\Delta TPS$ and $\Delta RPQ$.
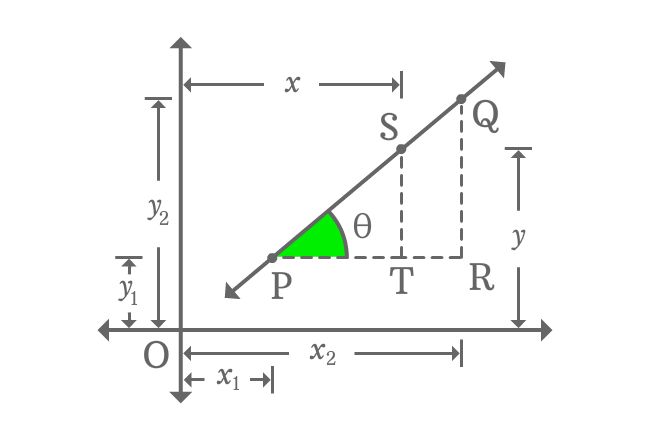
According to $\Delta TPS$
$m \,=\, \tan{\theta} \,=\, \dfrac{ST}{PT}$
$\implies m \,=\, \dfrac{OS-OT}{OT-OP}$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\, m \,=\, \dfrac{y-y_{1}}{x-x_{1}}$
We also know that $m \,=\, \dfrac{y_{2}-y_{1}}{x_{2}-x_{1}}$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\, \dfrac{y-y_{1}}{x-x_{1}} \,=\, \dfrac{y_{2}-y_{1}}{x_{2}-x_{1}}$
It can written further as follows.
$y-y_{1} \,=\, \dfrac{y_{2}-y_{1}}{x_{2}-x_{1}}(x-x_{1})$
It is a linear equation in terms of coordinates of two points in algebraic form.
A free math education service for students to learn every math concept easily, for teachers to teach mathematics understandably and for mathematicians to share their maths researching projects.
Copyright © 2012 - 2025 Math Doubts, All Rights Reserved