$\csc{(45^°)}$ Proof
The value of cosecant of $45$ degrees can be derived in trigonometry and also can derive in theoretical and practical approaches of geometry.
Theoretical approach
Theoretically, the value of cosecant of angle $45$ degrees can be derived exactly in geometry but we must know the direct geometrical relation between lengths of opposite and adjacent sides. When angle of right triangle is $45^°$, then the lengths of opposite and adjacent sides are equal. This property is used to derive the exact value of $\csc{(50^g)}$ in irrational form.

In $\Delta QPR$, the length of both opposite and adjacent side is denoted by $l$ and the length of hypotenuse is represented by $r$. Now, write relation between all three sides in mathematical form by Pythagorean Theorem.
${PQ}^2 = {PR}^2 + {QR}^2$
$\implies r^2 = l^2 + l^2$
$\implies r^2 = 2l^2$
$\implies r = \sqrt{2}.l$
$\implies \dfrac{r}{l} = \sqrt{2}$
In this case, $r$ and $l$ are lengths of hypotenuse and opposite side (or adjacent side) respectively.
$\implies \dfrac{Length \, of \, Hypotenuse}{Length \, of \, Opposite \, side} = \sqrt{2}$
When angle of right triangle is $\dfrac{\pi}{4}$, the ratio of lengths of hypotenuse to opposite side is called cosecant of angle $45$ degrees.
$\therefore \,\,\, \csc{(45^°)} = \sqrt{2}$
$\csc{(45^°)} = \sqrt{2} = 1.4142135623\ldots$
Practical approach
You can even find the value of cosecant of angle $45$ degrees even though you don’t know the geometric properties between sides of the right triangle when angle of the triangle is $45^°$. It can be done on your own by constructing a right triangle with $\dfrac{\pi}{4}$ by geometric tools.

- Identify a point ($M$) on plane and draw a horizontal line from it.
- Coincide point $M$ with centre of protractor and also coincide right side base line of protractor with horizontal line. Then, mark a point at $45$ degrees angle on plane.
- Draw a straight line from point $M$ through $45$ degrees angle line by ruler.
- Set compass to any length. In this case, compass is set to $6 \, cm$ by ruler. Now, draw an arc on $45^°$ line from point $M$ and the arc cuts the $45^°$ line at point $N$.
- From $N$, draw a perpendicular line to horizontal line and it cuts the horizontal line at point $O$. In this way, the right triangle $OMN$ is constructed geometrically.
The $\Delta OMN$ can be used to evaluate the exact value of $\csc{\Big(\dfrac{\pi}{4}\Big)}$ by calculating the ratio of lengths of hypotenuse to opposite side when angle of right triangle is $\dfrac{\pi}{4}$.
$\csc{(45^°)} = \dfrac{Length \, of \, Hypotenuse}{Length \, of \, Opposite \, side}$
$\implies \csc{(45^°)} \,=\, \dfrac{MN}{ON}$
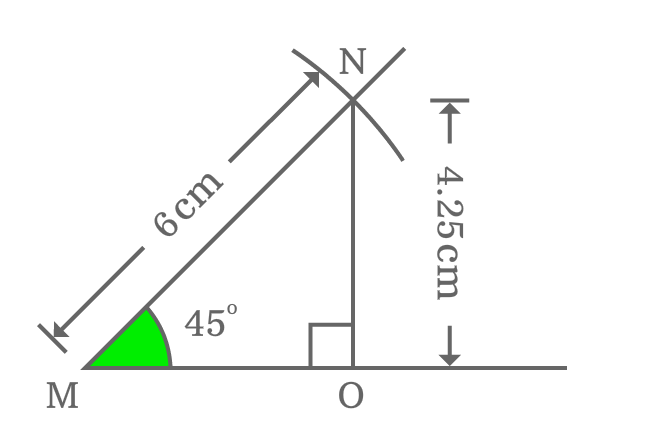
The $\Delta OMN$ is actually constructed by taking the length of hypotenuse as $6 \, cm$ but the length of opposite side is unknown.
Now, measure the length of opposite side by ruler and it will be nearly $4.25 \, cm$.
$\implies \csc{(45^°)} \,=\, \dfrac{MN}{ON} = \dfrac{6}{4.25}$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\, \csc{(45^°)} \,=\, 0.411764706\ldots$
Trigonometric approach
The value of cosecant of angle $50^g$ can also be derived by the reciprocal identity of sine function.
$\csc{(45^°)} = \dfrac{1}{\sin{(45^°)}}$
Now, substitute the exact value of sin of 45 degrees in fraction form.
$\implies \csc{(45^°)} = \dfrac{1}{\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}}$
$\implies \csc{(45^°)} = 1 \times \dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{1}$
$\implies \csc{(45^°)} = 1 \times \sqrt{2}$
$\,\,\, \therefore \,\,\,\,\,\, \csc{(45^°)} = \sqrt{2}$
Verdict
According to theoretical geometric approach and trigonometric approach, the exact value of cosecant of angle $45$ degrees is $\sqrt{2}$ or $1.4142135623\ldots$ but its value is $0.411764706\ldots$ as per practical geometric method.
There is some difference between values of cosecant of $45$ degrees when the value of theoretical geometric approach is compared with practical geometric approach. Due to some error in measuring the length of opposite side, the value of cosecant of $45$ degrees from practical geometric method differs with the exact value of cosecant of $45$ degrees.
The approximate value of $\csc{\Big(\dfrac{\pi}{4}\Big)}$ is often considered as $1.4142$ in mathematics.
